A Machine Learning-Based Predictive Model for Outcome of Covid-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients
I. Revuelta1, F. Santos-Arteaga2, D. Di Caprio3, E. Montagud-Marrahi1, F. Cofan1, J. Torregrosa1, M. Bodro4, A. Moreno4, P. Ventura-Aguiar1, D. Cucchiari1, N. Esforzado1, G. Piñeiro1, J. Ugalde-Altamirano1, J. Campistol1, A. Alcaraz5, B. Bayès1, E. Poch1, F. Oppenheimer1, F. Diekmann1
1Department of Nephrology and Kidney Transplant, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona, Spain, 2Faculty of Economics and Management, Free University of Bolzano, Bolzano, Italy, 3Department of Economics and Management, University of Trento, Trento, Italy, 4Department of Infectious Diseases, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona, Spain, 5Department of Urology, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona, Spain
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 315
Keywords: Economics, Kidney transplantation, Mortality, Prediction models
Topic: Clinical Science » Organ Inclusive » Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Social Media in Transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Disparities in Access and Machine Learning Outcomes in Solid Organ Transplantation
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 8, 2021
Session Time: 4:30pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:00pm-5:05pm
Presentation Time: 5:00pm-5:05pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Health systems need tools to deal with COVID-19, especially for high-risk population,such as transplant recipients. Predictive models are necessary to improve management of patients and optimize resources.
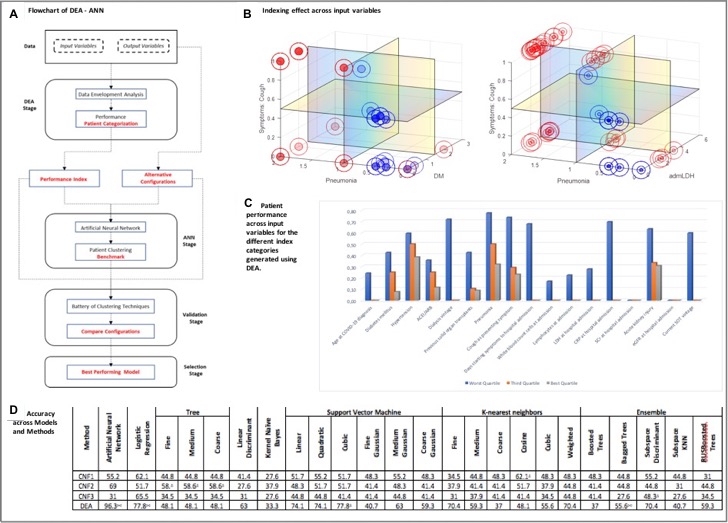
*Methods: A retrospective study of hospitalized transplant patients due to COVID-19 was evaluated(March 3-April 24,2020). Admission data were integrated to develop a prediction model to evaluate a composite-event defined as Intensive Care Unit admission or intensification treatment with antiinflamatory agents. Predictions were made using a Data Envelopment Analysis(DEA)-Artificial Neural Network(ANN) hybrid, whose accuracy relative to several alternative configurations has been validated through a battery of clustering techniques.
*Results: Of 1006 recipients with a planned or an unscheduled visit during the observation period, thirty-eight were admitted due to COVID-19. Twenty-five patients(63.2%) exhibited poor clinical course(mortality rate:13.2%), within a mean of 12 days of admission stay. Cough as a presenting symptom(P=0.000), pneumonia(P=0.011), and levels of LDH(P=0.031) were admission factors associated with poor outcomes. The prediction hybrid model working with a set of 17 input variables displays an accuracy of 96.3%, outperforming any competing model, such as logistic regression(65.5%) and Random forest(denoted by Bagged Trees,44.8%). Moreover, the prediction model allows us to categorize the evolution of patients through the values at hospital admission.
*Conclusions: The prediction model based in Data Envelopment Analysis-Artificial Neural Network hybrid forecasts the progression towards severe COVID-19 disease with an accuracy of 96.3%, and may help to guide COVID-19 management by identification of key predictors that permit a sustainable distribution of resources in a patient-centered model. Improving efficiency and patient parformance in the AAN with DEA, we can get high accurancy even with no-big cohorts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Revuelta I, Santos-Arteaga F, Caprio DDi, Montagud-Marrahi E, Cofan F, Torregrosa J, Bodro M, Moreno A, Ventura-Aguiar P, Cucchiari D, Esforzado N, Piñeiro G, Ugalde-Altamirano J, Campistol J, Alcaraz A, Bayès B, Poch E, Oppenheimer F, Diekmann F. A Machine Learning-Based Predictive Model for Outcome of Covid-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-machine-learning-based-predictive-model-for-outcome-of-covid-19-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress