A Dose Dependent Effect of Varying Tacrolimus Concentrations on Cytomegalovirus Viral Specific T Cell Interferon Gamma Expression
H. L. Kleiboeker1, M. R. Jorgenson1, R. O. Meyers2, O. Ganz2, S. Parajuli3, J. Galipeau4
1Pharmacy, University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics, Madison, WI, 2Program for Advanced Cell Therapy, University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics and School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI, 3Medicine, Division of Nephrology, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI, 4Medicine, Division of Hematology and Oncology, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 691
Keywords: Immunosuppression
Topic: Clinical Science » Infection Disease » 24 - All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis)
Session Information
Session Name: All Infections (Excluding Kidney & Viral Hepatitis) I
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 4, 2022
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Tacrolimus, considered the backbone of transplant immunosuppression, is associated with increased risk of viral infections, including cytomegalovirus (CMV), due to its potent inhibitory effect on T cells. Dose-dependent relationships between tacrolimus concentration and expression of CMV specific T lymphocyte (VST) intracellular IL-2 and IFNγ have not been characterized.
*Methods: Manufactured CMV VST cells were characterized by flow cytometry after preparation and collection. Cells were manufactured and purified per Miltenyi Biotec Cytokine Capture System. Primary objective was to evaluate increasing concentrations of tacrolimus on cell viability and percent CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ IFNγ expression. Cells were treated with increasing concentrations of tacrolimus (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 ng/mL) in triplicate wells. Additional wells seeded for controls. After incubation, CMV pp65 added to each well for in vitro stimulation of pp65-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Cells were washed and stained with antibody cocktail containing CD3 FITC (BD), CD4 VioBlue (Miltenyi Biotec) and CD8 APC (BD). Cells were fixed and permeabilized, then IFNγ PE (BD) and IL2 APC-Vio770 (Miltenyi Biotec) antibodies were added during intracellular staining. Cells were washed and analyzed using MACSQuant Analyzer.
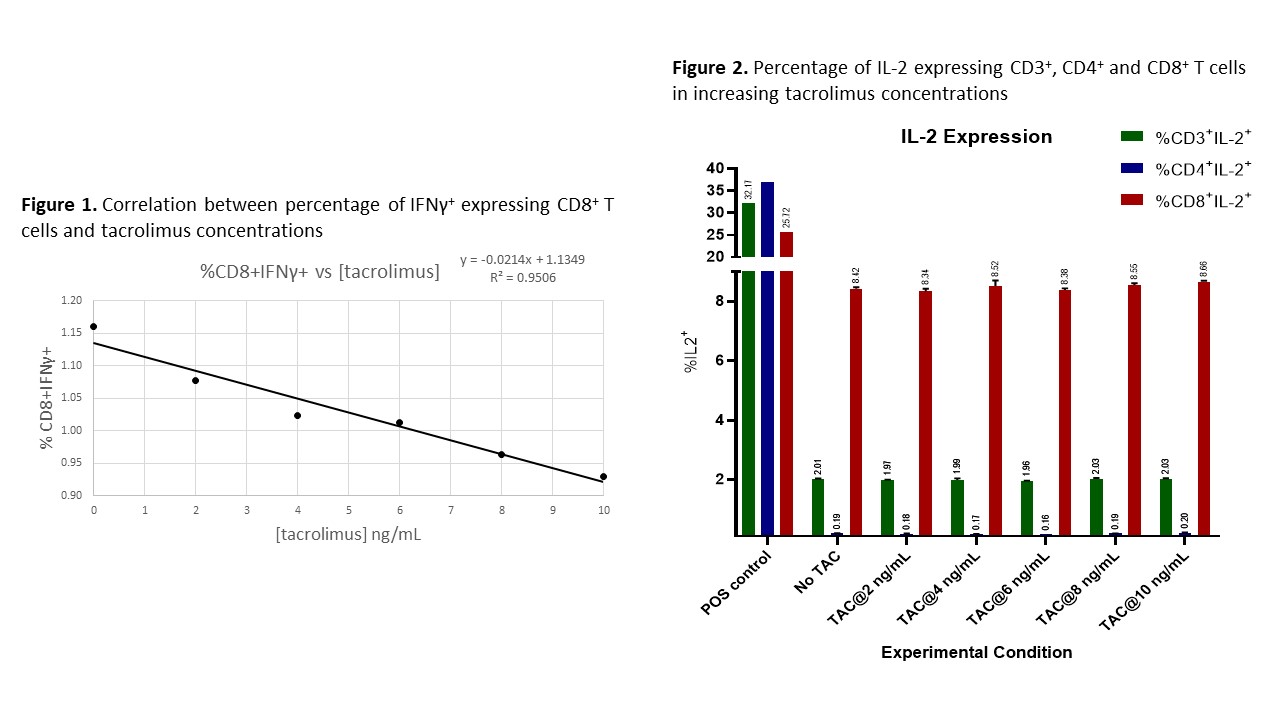
*Results: Target cell bags contained 1.24 x 106 viable WBCs (4.56 x 105 CD3+). Non-target cell bags contained 0.6 x 109 viable WBCs (0.4 x 109 CD3+). A linear, dose-dependent negative correlation in the mean percentage of IFNγ+ expressing CD8+ T cells over the increasing range of tacrolimus concentration was observed (figure 1). A correlation between IL-2 expressing T cells and increasing tacrolimus concentrations was not observed (figure 2).
*Conclusions: Higher tacrolimus concentrations result in functional impairment of CMV VST cells via reductions in T cell IFNγ expression. IL-2 expression was not affected, but this may have been a result of inhibitory feedback in selected media. Further research is needed regarding ideal tacrolimus concentrations to optimize VST function and increase the therapeutic potential of allogeneic donor CMV-specific T lymphocytes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kleiboeker HL, Jorgenson MR, Meyers RO, Ganz O, Parajuli S, Galipeau J. A Dose Dependent Effect of Varying Tacrolimus Concentrations on Cytomegalovirus Viral Specific T Cell Interferon Gamma Expression [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-dose-dependent-effect-of-varying-tacrolimus-concentrations-on-cytomegalovirus-viral-specific-t-cell-interferon-gamma-expression/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress