A Cost Effectiveness Analysis of Adherence Promotion Strategies to Improve Rejection Rates in Adolescent Kidney Transplant Patients
C. Varnell1, K. Rich1, A. Modi1, D. Hooper1, M. Eckman2
1Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH, 2University of Cincinnati School of Medicine, Cincinnati, OH
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 445
Keywords: Economics, Immunosuppression, Pediatric
Topic: Clinical Science » Ethics » 22 - Psychosocial and Treatment Adherence
Session Information
Session Name: Psychosocial and Treatment Adherence
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Tuesday, June 7, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:40pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-3:40pm
Location: Hynes Room 311
*Purpose: In adolescents with a kidney transplant, non-adherence increases the risk of graft loss. Adherence promotion interventions improve adherence and rejection rates, but perceived cost remains a barrier to clinical implementation.
*Methods: We examined the cost-effectiveness of a single center medication adherence promotion system (MAPS) that was associated with a 45% reduction in rejection rates over a two-year period in a single center as a model to assess the cost-effectiveness of adherence promotion strategies in general. We used a Markov state transition decision model with a health care system perspective and a lifelong time horizon. Effectiveness was measured in quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) and costs measured in 2020 US dollars.
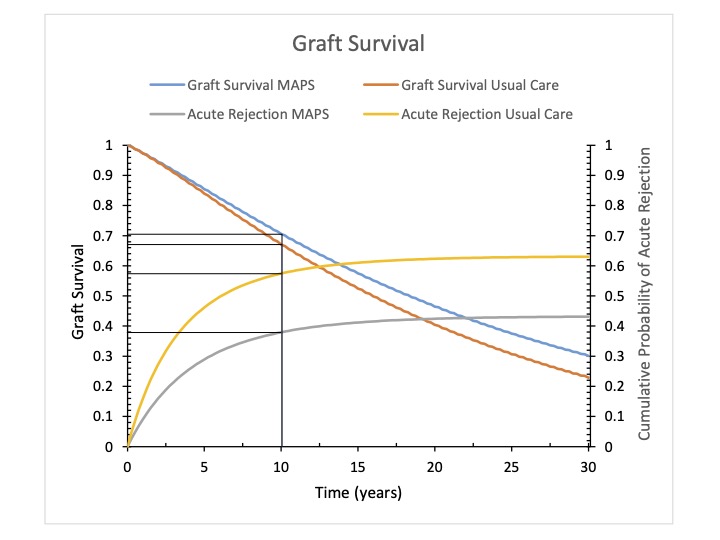
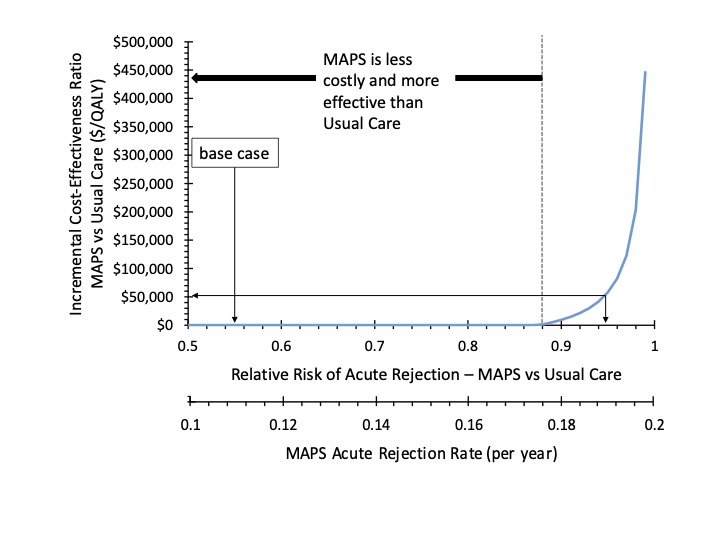
*Results: In base-case analysis, post-transplant care with MAPS was more effective and less costly than usual care due to reduced acute rejection and increased graft survival with associated cost savings (Fig1). MAPS cost $9,106 per patient less than usual care and resulted in a gain of 0.32 QALYs. In sensitivity analyses, MAPS dominates usual care by being less costly and more effective so long as the RR for rejection is < 0.88. As efficacy declines (RR >0.88) the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio increases (Fig2). In probabilistic sensitivity analyses, MAPS was cost saving 100% of the time. Strategies that reduce the risk of rejection by as little as 3% with similar cost are highly cost-effective. Interventions demonstrating greater reductions in rejection remain highly cost-effective as long as the start-up cost attributable to a single patient is less than $25,000 and the ongoing annual program cost per patient is less than $1,880 per year.
*Conclusions: This study describes a model that can be applied to study the cost-effectiveness of adherence promotion strategies. Given the significant cost and impact on quality of life associated with treatment of acute rejection and graft failure, even adherence promotion strategies that only modestly reduce acute rejection rates can have significant impact on health and quality of life at substantial cost-savings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Varnell C, Rich K, Modi A, Hooper D, Eckman M. A Cost Effectiveness Analysis of Adherence Promotion Strategies to Improve Rejection Rates in Adolescent Kidney Transplant Patients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-cost-effectiveness-analysis-of-adherence-promotion-strategies-to-improve-rejection-rates-in-adolescent-kidney-transplant-patients/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress