A Cost Comparison for Telehealth Utilization in the Kidney Transplant Waitlist Evaluation Process at a VA Center.
Renal Transplantation, Tennessee Valley Healthcare System, U.S. Dept Veterans Affairs, Nashville
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 322
Keywords: Economics, Screening, Waiting lists
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Disparities in Organ Transplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:42pm
Location: E353C
Background: The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has made efforts to improve access by increasing telehealth utilization. There have been limited publications on telehealth in transplantation with no prior reports of telehealth-related costs for pre-transplant evaluations.
Methods: Patients approved for kidney transplant waitlist evaluation at the Nashville VA from March 2013 thru March 2016 were included. Patients were seen initially via telehealth or in-person with subsequent decision-making per Figure 1.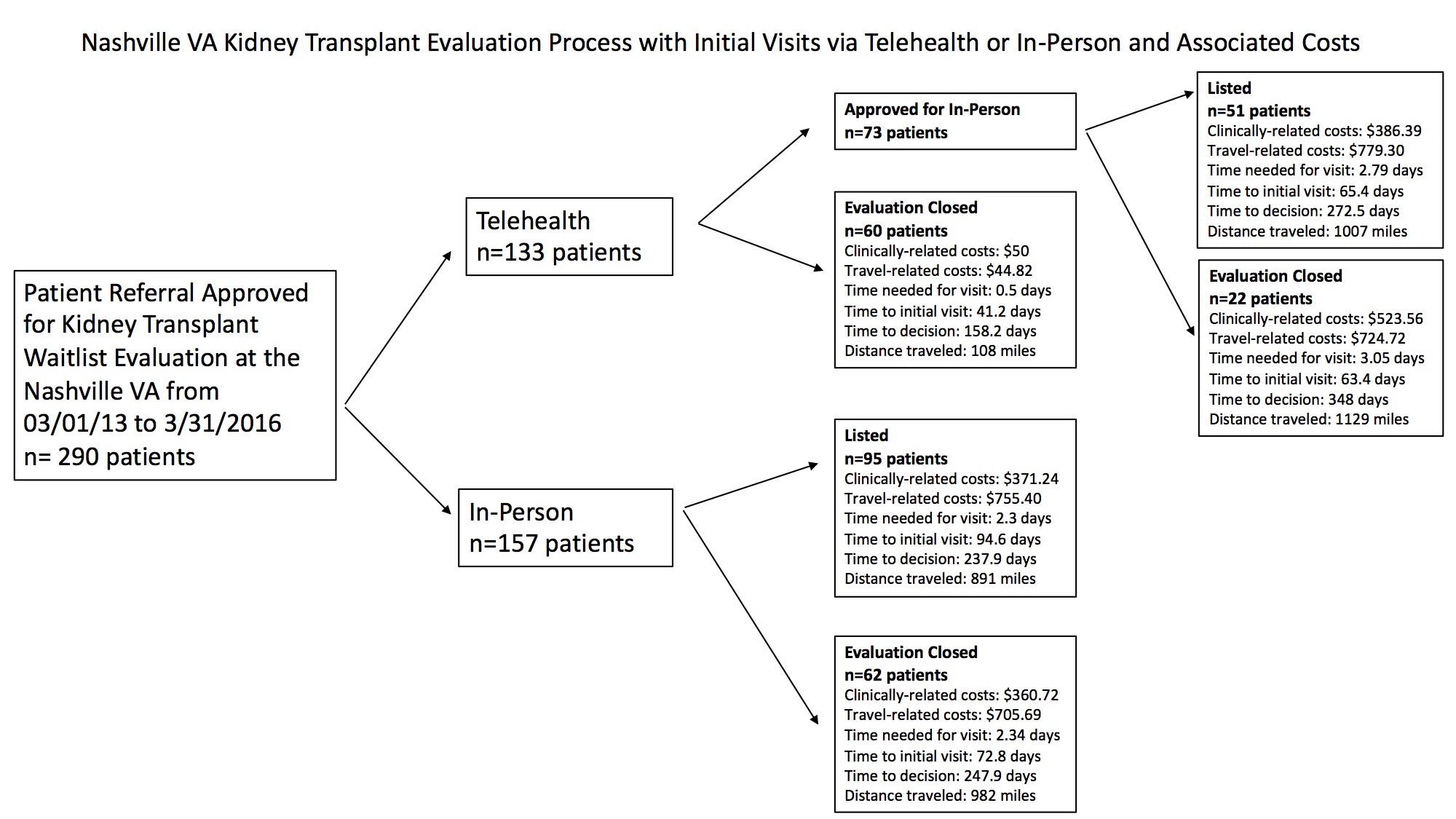 Clinically-related costs for visit type and dialysis needs on the day of evaluation were determined. Travel-related costs and time metrics were also obtained (Figure 1). Comparisons were made using t-tests.
Clinically-related costs for visit type and dialysis needs on the day of evaluation were determined. Travel-related costs and time metrics were also obtained (Figure 1). Comparisons were made using t-tests.
Results: Thirty-seven months of data were included for 290 patients approved for waitlist evaluation visits from 03/01/13 through 03/31/16. All categories of costs in this analysis, including visit costs, dialysis costs, travel (either flight and/or mileage) costs, taxi costs, and hotel costs, were significantly less for the cohort initially evaluated by telehealth (p<0.001).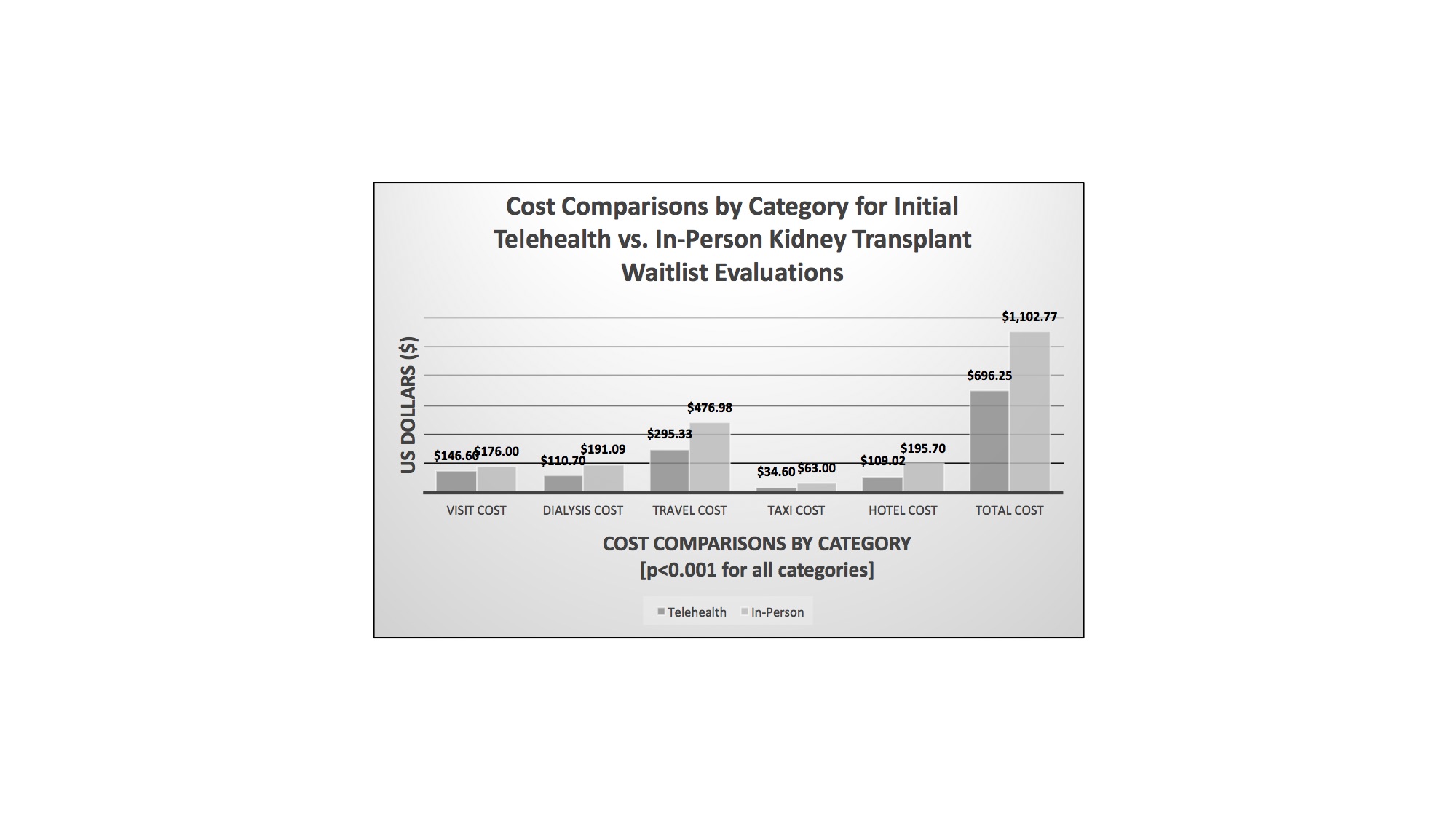 Total cost per patient was $696.25 vs. 1102.77 for the cohort initially evaluated by telehealth vs. in person (p<0.001). The time needed to complete an evaluation (1.8 vs. 2.3 days, p<0.001) and the time to initial evaluation (54.2 vs. 86.0 days, p<0.001) were significantly less if in the telehealth cohort, although the time to decision was not statistically less for the telehealth group vs. in-person (210.8 vs. 241.9 days, p=0.15).
Total cost per patient was $696.25 vs. 1102.77 for the cohort initially evaluated by telehealth vs. in person (p<0.001). The time needed to complete an evaluation (1.8 vs. 2.3 days, p<0.001) and the time to initial evaluation (54.2 vs. 86.0 days, p<0.001) were significantly less if in the telehealth cohort, although the time to decision was not statistically less for the telehealth group vs. in-person (210.8 vs. 241.9 days, p=0.15).
Conclusion: As telemedicine applications continue to proliferate, we present our experience with telehealth for initial kidney transplant waitlist evaluations with associated cost and time expense data showing significant resource utilization improvements.
CITATION INFORMATION: Forbes R, Rybacki D, Johnson T, Shaffer D, Hale D. A Cost Comparison for Telehealth Utilization in the Kidney Transplant Waitlist Evaluation Process at a VA Center. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Forbes R, Rybacki D, Johnson T, Shaffer D, Hale D. A Cost Comparison for Telehealth Utilization in the Kidney Transplant Waitlist Evaluation Process at a VA Center. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-cost-comparison-for-telehealth-utilization-in-the-kidney-transplant-waitlist-evaluation-process-at-a-va-center/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
