Financial Cost of Cold Ischemia Time in Kidney Transplantation.
1Surgery, Univ. of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN
2Biostatistics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN
3Health Policy & Management, Univ. of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 271
Keywords: Allocation, Economics, Kidney, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Acute Kidney Injury and Recovery after Transplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Location: Ballroom C
PURPOSE: A new kidney allocation system (KAS) was implemented in December 2014 using the kidney donor profile index (KDPI), which prioritizes historically-disadvantaged populations. While KAS aims to maximize the equitable sharing of kidney allografts, concerns remain that its implementation through wider geographical sharing may lead to increased cold ischemia time (CIT) and CIT-associated adverse effects, namely delayed graft function (DFG), and ultimately, transplant-related costs.
METHODOLOGY: Between 2006 and 2014, 1495 kidney transplants (KTx) were performed at our institution. Donor and recipient demographics, intraoperative parameters, short- and long-term outcomes and hospitalization cost data were collected. A linear regression model was constructed adjusting for recipient age, race, gender, pre-KTx hemodialysis (HD) status, KDPI, and donor type (DD, LD) to assess the impact of CIT on DGF, LOS (LOSTx) and cost (cTx) of transplant admission, and overall 1-year post-transplant in-hospital LOS (LOS1Y) and cost (c1Y).
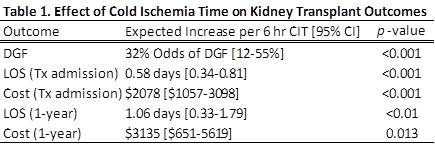
RESULTS: A total of 1200 KTx recipients had financial records available for analysis. Median age at transplant was 48.7 years (IQR 32.6, 59.7). The majority of our patients were male (62.5%), Caucasian (80.9%) and on pre-KTx HD (60%); 43% received a DD kidney. In multivariate analysis, CIT was associated with increased DGF (p<0.001), LOSTx (p<0.001), cTx (p<0.001), LOS1 (p<0.01) and c1Y (p=0.013). The incremental effect of CIT on KTx outcomes is listed in Table 1.
CONCLUSION: One of the unintended consequences of KAS is the prolongation of CIT, which has the potential to increase DGF rates. In turn, we have seen increased DGF rates lead to increased LOS and hospital costs.
CITATION INFORMATION: Serrano O, Vock D, Payne W, Dunn T, Chinnakotla S, Kandaswamy R, Pruett T, Matas A, Feldman R, Finger E. Financial Cost of Cold Ischemia Time in Kidney Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Serrano O, Vock D, Payne W, Dunn T, Chinnakotla S, Kandaswamy R, Pruett T, Matas A, Feldman R, Finger E. Financial Cost of Cold Ischemia Time in Kidney Transplantation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/financial-cost-of-cold-ischemia-time-in-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed February 5, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
