The Higher Cost of Donation After Circulatory Death Liver Transplantation Starts with Acquisition Costs: A Single Center Comparison Liver Acquisition Fees by Donor Type
1Baylor Scott and White Research Institute, Allen, TX, 2Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, TX, 3Baylor University Medical Center, Fort Worth, TX, 4Baylor Simmons Transplant Inst, Dallas, TX
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1330
Keywords: Allocation, Circulatory Death, Donors, non-heart-beating, Economics
Topic: Clinical Science » Public Policy » 21 - Non-Organ Specific: Public Policy & Allocation
Session Information
Session Name: Non-Organ Specific: Public Policy & Allocation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Donation after circulatory death (DCD) donors are an increasing proportion of deceased donor population in the US. One drawback of DCD donors is that many don’t expire in time for organ donation resulting in dry runs. We hypothesized that not only do DCDs increase the time spent by transplant surgeons in the acquisition of organs but they also have higher acquisition costs per transplanted liver.
*Methods: We collected the OPO and flight invoices for all donors for our center from July 1, 2019 through Oct 30, 2020. We also collected donor and recipient data from UNOS. We compared the donor and recipient characteristics and costs of transplantation between DCD and DBD donors.
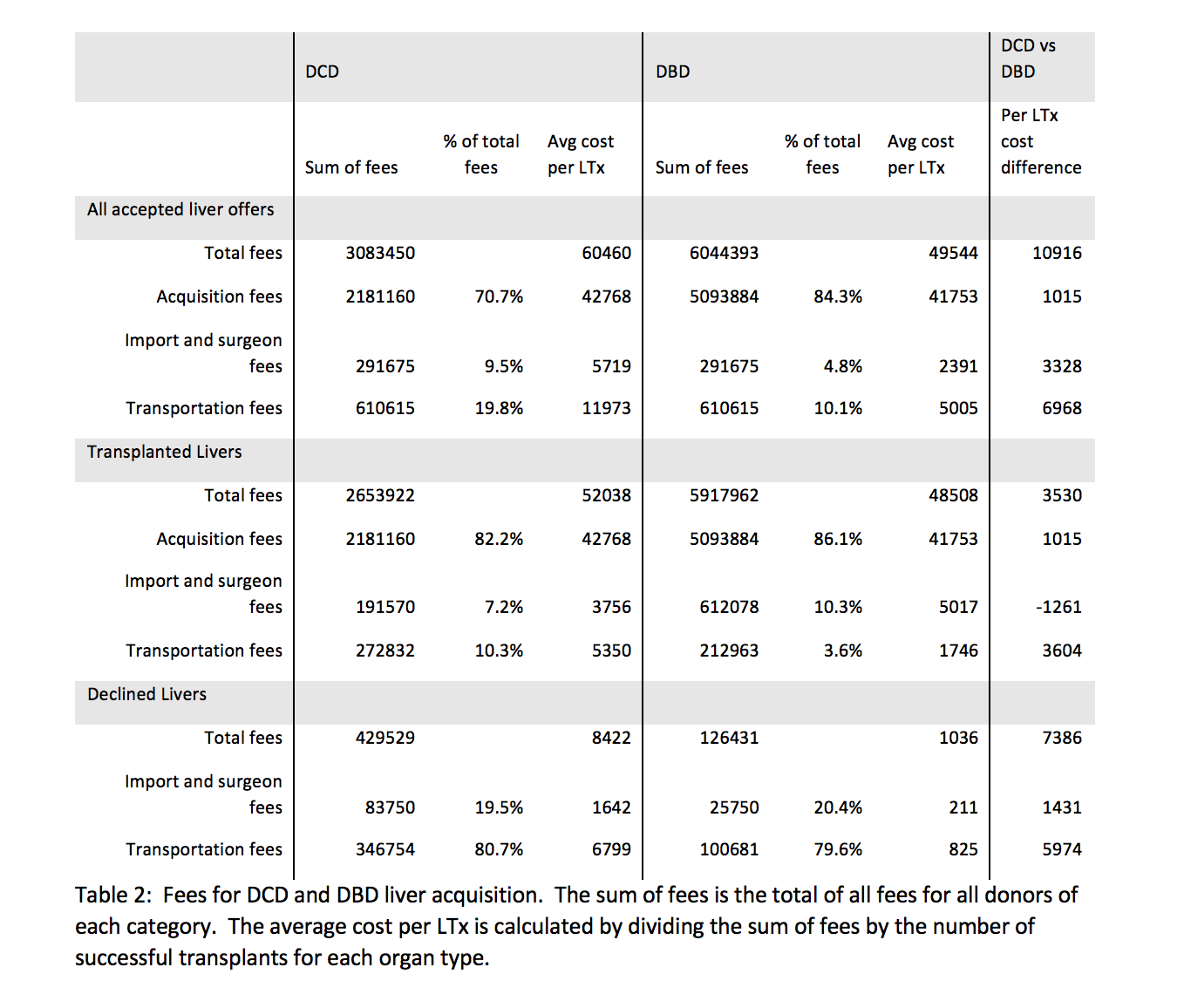
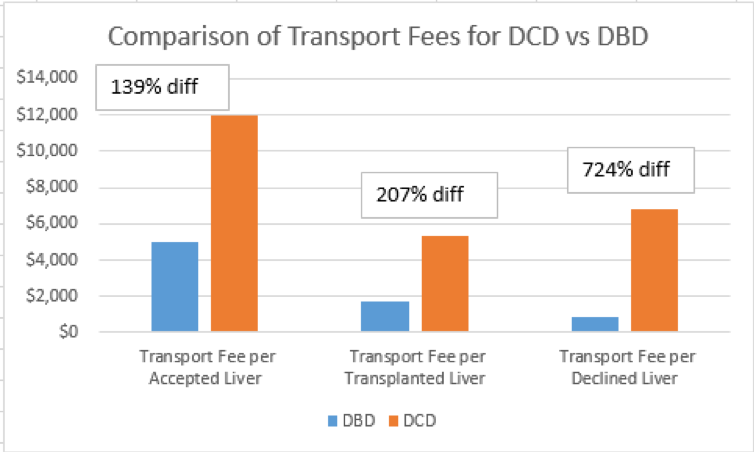
*Results: 55.4% of DCD donors were imports compared to 47% of DBD liver offers (p = 0.009). 75.9% of DCD donors used flight transportation compared to 51.5% of DBD donors (p <0.001). 38.6% of DCD livers were declined in the OR versus 6.2% of DBD livers (p <0.001). The absolute difference in cost per transplant was $10,916, or 22% higher for DCD donors compared to DBD liver transplants. The main contributors to the difference in liver acquisition cost were the transportation, import, and surgeon fees for declined DCD livers ($8,422 [DCD] vs. $1,036 [DBD]).
*Conclusions: The per completed transplant for DCD liver acquisition was 22% higher than for DBD liver acquisition due to the large number of dry runs that incurred both transportation and import fees. Strategies to reduce the cost of dry runs include utilizing local recovery, or when sending a team, using ground transportation and commercial flights.
| DCD (n=83) n(%) | DBD (n=130) n(%) | p value | |
| Import | 46 (55.4) | 47 (36.2) | .009 |
| Flight transportation | 63 (75.9) | 54 (41.5) | <.001 |
| Region4 | 77 (92.8) | 121 (93.1) | >.99 |
| Decline in OR | 32 (38.6) | 8 (6.2) | <.001 |
| Recipient MELD (median, IQR) | 26 (22-30) | 23 (18.5-26 | <.001 |
| Recipient match sequence (median, IQR) | 9 (4-23.5) | 26 (6.5-74) | <.001 |
| Distance from donor to recipient (median, IQR) | 180 (0-207) | 164 (80-207) | .01 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reddy V, Asrani S, Trotter J, Ruiz R, Lee S, Martinez E, Onaca N, McKenna G, Gupta A, Fernandez H, Bayer J, Testa G, Wall A. The Higher Cost of Donation After Circulatory Death Liver Transplantation Starts with Acquisition Costs: A Single Center Comparison Liver Acquisition Fees by Donor Type [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-higher-cost-of-donation-after-circulatory-death-liver-transplantation-starts-with-acquisition-costs-a-single-center-comparison-liver-acquisition-fees-by-donor-type/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress