Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Post Antibody Mediated Rejection Treatment in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients: Interim Report from the Paramour “PediAtric Renal AMr Outcomes” Study
1Maria Fareri Children's Hospital, Valhalla, NY, 2Emory University, Atlanta, GA, 3The Children's Hospital at Montefiore, Bronx, NY, 4Children's Hospital of Michigan, Detroit, MI, 5Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH, 6Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, 7LSU Health New Orleans, New Orleans, LA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-045
Keywords: Infection, Pediatric, Prophylaxis, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney: Pediatrics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Universal guidelines do not exist for post antibody mediated rejection (AMR) treatment antimicrobial prophylaxis (ppx) in pediatric kidney transplant (KT) recipients. We sought to determine the patterns of antimicrobial ppx and incidence of infections in this population.
*Methods: We collected data on AMR treatment, ppx patterns, and infection rates in KT recipients <18 years old with biopsy proven AMR between 12/31/2009-12/31/2017 and followed for 12 consecutive months at 6 US centers within the Pediatric Nephrology Research Consortium.
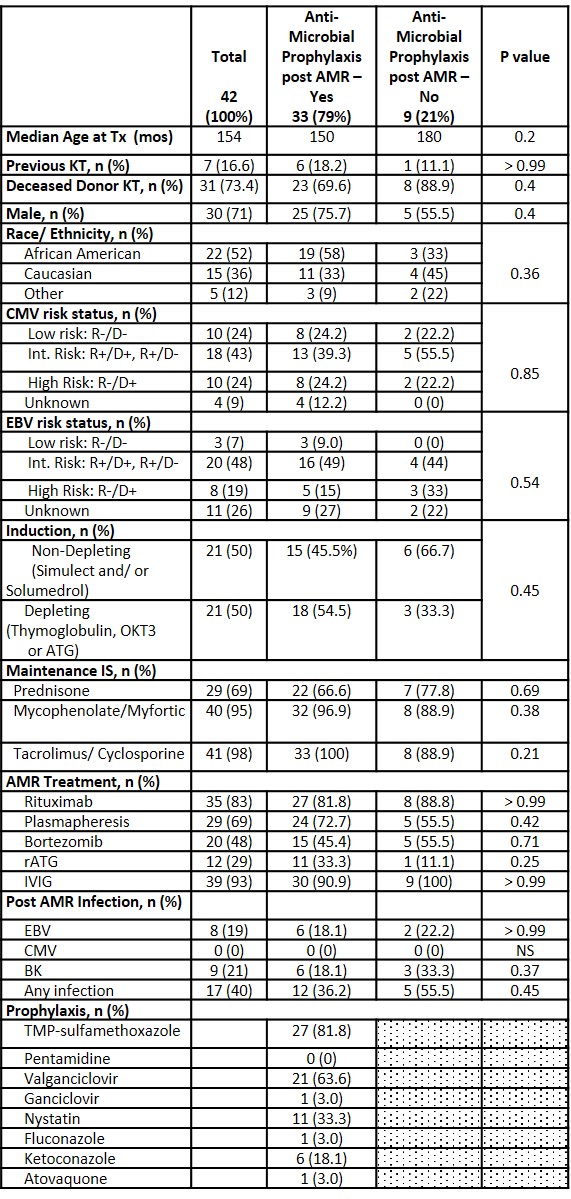
*Results: We reviewed 42 AMR episodes to date. Overall, 78% of KT recipients received antimicrobial ppx post AMR treatment with highest % noted in those treated with rabbit antithymocyte globulin (rATG) at 92%. Patients who received ppx post AMR treatment did not differ from those who did not with regards to age, gender, donor type, race, donor source, CMV or EBV donor-recipient mismatch, induction or maintenance immunosuppression. Comparison based on ppx exposure is shown in Table. AMR treatment included rituximab, plasmapheresis, bortezomib, rATG, and IVIg. Individual AMR treatment modality exposure did not differ between those receiving ppx and those who did not. In those receiving ppx, coverage consisted of PCP ppx in 85% (median duration 6 mo [range 2-12]), antiviral (CMV) ppx in 73% (6 mo [2-12]) and antifungal ppx in 55% (3 mo [1-6]). BK viremia developed in 21% of patients. EBV viremia was similar in both groups at 18.1% and 22.2%, respectively. No cases of CMV viremia were noted. KT recipients who developed viremia post AMR treatment were more likely to have received rATG (41.6% vs 23.3%) and less likely to have received rituximab (66.7% vs. 90%) compared to those without viremia. Of those that received rituximab, BK viremia was more common than EBV viremia (66% vs. 50%).
*Conclusions: The majority of pediatric KT recipients in this cohort received antimicrobial ppx post AMR treatment. A slightly higher percentage of those who did not receive ppx developed post AMR treatment infection though the difference was not significant. Larger studies are needed to identify specific risk and protective factors for post AMR infection and inform rational post AMR prophylaxis regimens.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Solomon S, Garro R, Hayde N, Jain A, Kallash M, Twombley K, Ashoor I. Antimicrobial Prophylaxis Post Antibody Mediated Rejection Treatment in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients: Interim Report from the Paramour “PediAtric Renal AMr Outcomes” Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/antimicrobial-prophylaxis-post-antibody-mediated-rejection-treatment-in-pediatric-kidney-transplant-recipients-interim-report-from-the-paramour-pediatric-renal-amr-outcomes-study/. Accessed February 16, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress