Estimating Opioid-Related Deaths from Toxicology Reports
C. Martinez, A. M. Zehner, A. Placona
United Network for Organ Sharing, Richmond, VA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A-230
Keywords: Donors, unrelated, Mortality
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Deceased Donor Management and Intervention Research
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The “Drug Intoxication” mechanism of death from the DDR is a proxy for opioid-related death. Previous investigations have leveraged this proxy to assess impact of the opioid epidemic in organ transplantation. This has some limitations such as classifying overdose of non-opioid drugs as an opioid overdose. Here we contrast an alternative proxy for estimating opioid-related deaths: toxicology reports with opioid screening as entered into free-text fields on DonorNet.
*Methods: We collected toxicology reports from DonorNet for all deceased donors since 2008 (N = 67,212 donors with non-missing toxicology reports). Of those, we identified 34,333 (51.1%) toxicology reports that appeared to be computer-generated with predictable formatting. Hence, we could programmatically parse these reports to search for opioid screening. In particular, we searched for testing of opiates, methadone, fentanyl, and several other opioids.
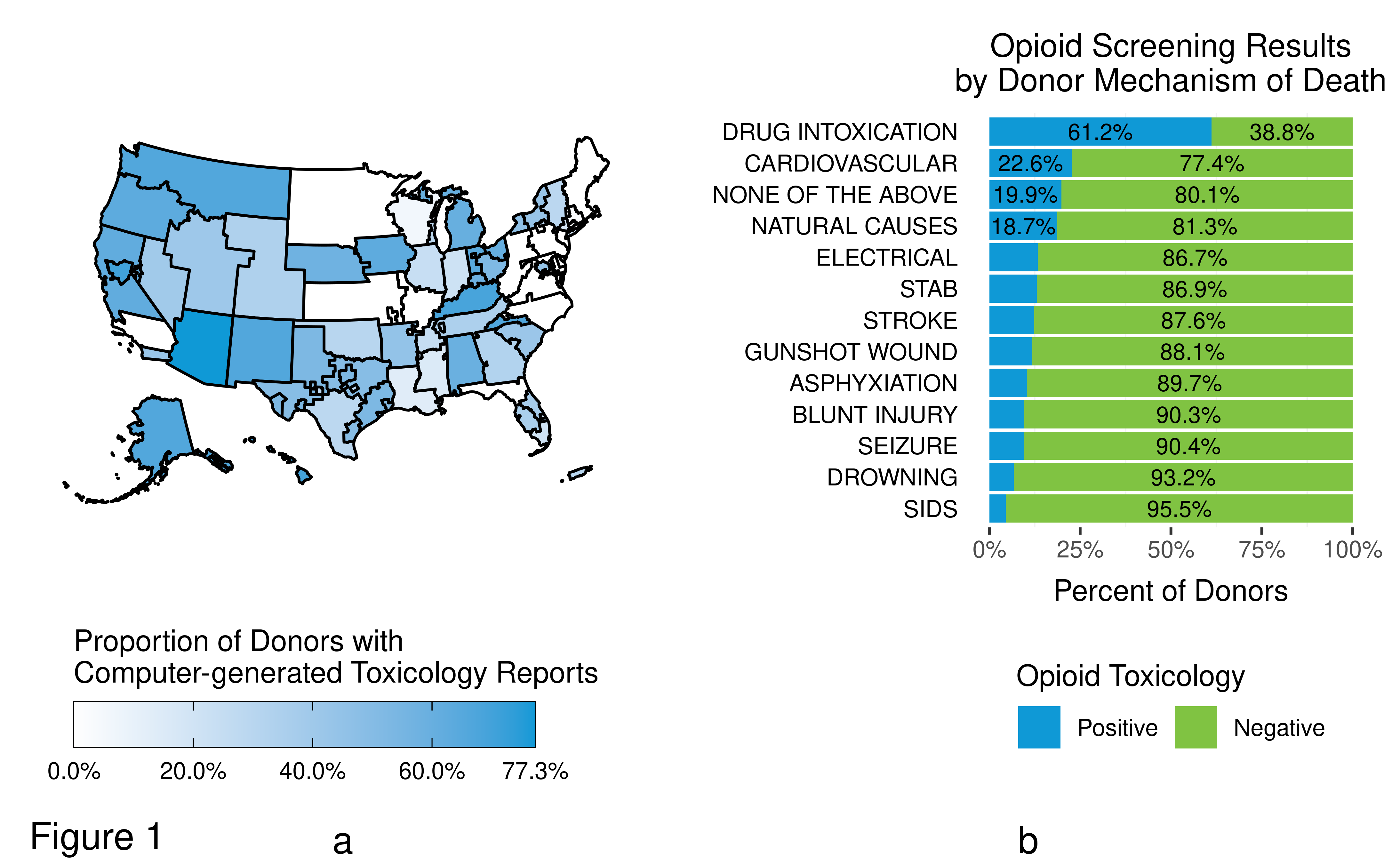
*Results: The percent of donors with computer-generated toxicology reports varied by DSA from 0% to 77.3% (Figure 1a). The majority (91.9%) of these reports tested for opioids.
The proportion of donors with positive opioid screenings ranged from 4.5% to 22.6% across all mechanisms of death except for death by Drug Intoxication in which 61.2% of donors tested positive (Figure 1b). The next category with the largest percentage of positive opioid screening was the Cardiovascular mechanism of death at 22.6% while the lowest is Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) at 4.5%.
*Conclusions: The Drug Intoxication mechanism of death as a proxy for opioid-related death may have two major limitations. First, we observed a sizable percentage (>38%) of donors under this mechanism of death in fact screen negative for opioids and thus may not qualify as an opioid-related death. Second, donors listed under other mechanisms of death have smaller but nonnegligible rates of positive opioid testing. Thus, potentially opioid-related deaths may be categorized under a mechanism of death other than Drug Intoxication.
There are limitations associated with the usage of toxicology reports from DonorNet. First, there may be selection bias, including geographical bias, in that not all donors have uploaded toxicology reports. Further, of all toxicology reports uploaded, we analyzed only a subset that had computer-generated formatting. Finally, even opioid-positive toxicology reports do not provide enough context to conclude that death was due to an opioid-related event. With these limitations in mind, this study highlights the need for a more refined and rigorous quantification of opioid-related deaths to understand the impact of the opioid epidemic on donor volume.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martinez C, Zehner AM, Placona A. Estimating Opioid-Related Deaths from Toxicology Reports [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/estimating-opioid-related-deaths-from-toxicology-reports/. Accessed February 8, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress