High Health Care Utilizers in Kidney Transplantation: Do You Know Your Frequent Flyers?
1Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Outcomes Sciences, Medical University of South Carolina`, Charleston, SC, 2General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics, Medical University of South Carolina`, Charleston, SC, 3Surgery and Ralph H. Johnson VAMC, Medical University of South Carolina`, Charleston, SC, 4Surgery, Medical University of South Carolina`, Charleston, SC, 5Clinical Pharmacy and Outcomes Sciences, Medical University of South Carolina`, Charleston, SC
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D202
Keywords: Multivariate analysis, Outcome, Prediction models, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Non-Organ Specific: Economics & Ethics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
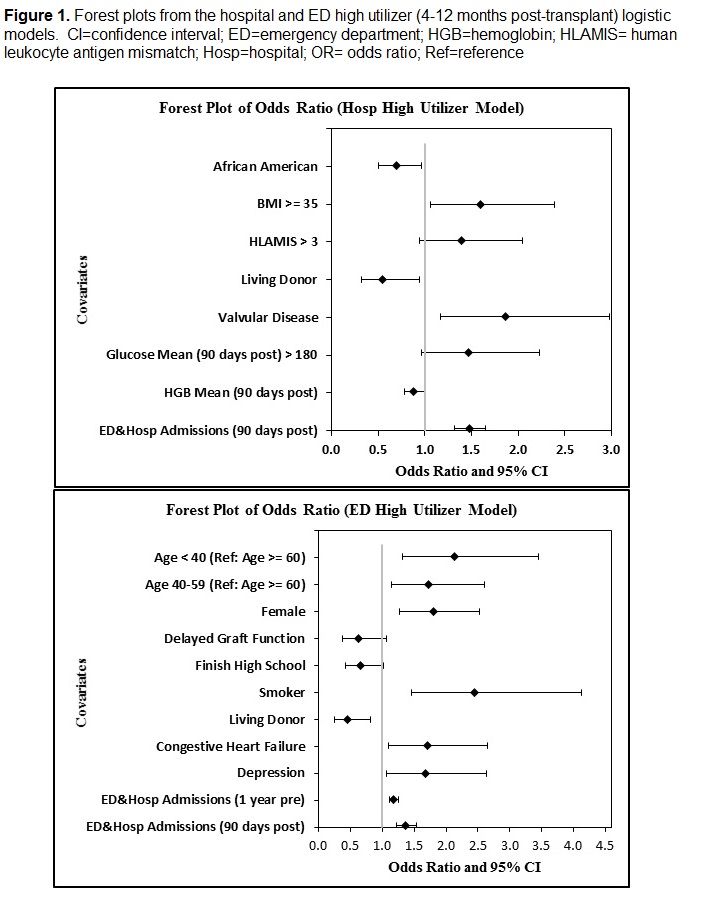
*Purpose: To assess high hospital inpatient [IP] admissions and emergency department [ED] utilization within a 9-month period after kidney transplantation in order to identify potential mutable factors for reducing post-transplant health care utilization.
*Methods: This was a 9-year retrospective study in adult kidney transplant recipients from 01/2007-12/2015. Patients with previous transplant, or graft loss or death within 3 months post-transplantation, were excluded. Comprehensive resource utilization data were retrieved from state All-Payer Public Use data files. Patients with ≥2 IP admissions or standalone ED visits within 4-12 months post-transplantation were classified as high IP or ED utilizers. Multivariable logistic regression models were used for examining associations of predictors with high IP or ED utilization.
*Results: Of 1,280 kidney recipients, 209 (16.3%) and 183 (14.3%) were categorized as IP and ED high utilizers; respectively. Factors significantly associated (Figure 1) with being a hospital IP high utilizer included valvular disease, BMI>35 at the time of transplant and IP/ED use within 3 months post-transplantation. IP/ED use within 3 months post-transplantation was also associated with being an ED high utilizer along with age<40 years or 40-59 years versus age>60 years, female, smoker at the time of transplant , congestive heart failure, depression and IP/ED use 1 year pre-transplantation.
*Conclusions: Hospital IP and ED utilization within a 9-month period after kidney transplantation is high and associated with sociodemographic factors, comorbidities, and healthcare utilization. Non-traditional transplant risk factors should be considered to better risk-stratify this kidney transplant population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Weeda E, Su Z, Taber D, Bian J, Morinelli TA, Pilch NA, Mauldin PD, DuBay DA. High Health Care Utilizers in Kidney Transplantation: Do You Know Your Frequent Flyers? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/high-health-care-utilizers-in-kidney-transplantation-do-you-know-your-frequent-flyers/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress