Everolimus (RAD001) Treatment Effect in Liver Transplantation – A Rational Approach To Quantify the mTOR Effect
The H2304 Study Group, Basel, Switzerland
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D1603
Background: 12M study results of study CRAD001H2304 (NCT00622869) demonstrated superior renal function and comparable efficacy, including fewer and less severe treated BPAR with everolimus (EVR) plus reduced exposure tacrolimus (rTAC) vs. standard exposure TAC (sTAC) in de novo liver transplant recipients (LTxR). Here, evidence of TAC exposure-efficacy response relationship and contribution of EVR to efficacy are shown.
Methods: 719 de novo LTxR received at 1M post LTx either EVR(C0 3-8 ng/mL) + rTAC(C0 3-5 ng/mL), or EVR(C0 6-10 ng/mL) with TAC Elimination or sTAC(C0 6-10 ng/mL). Individual time courses of TAC concentration were estimated using totality of TAC PK and dose administration data using a popPK approach. The relationship between predicted TAC concentrations and event rate was quantified. From this relationship, the effect of rTAC alone is estimated and compared to the effect of EVR+rTAC to demonstrate the compensatory effect of EVR.
Results: In the sTAC arm, 11/22 BPARs occurred while predicted TAC concentration was below the 25th percentile of the distribution in patients without events, vs only 3 events with concentrations above the 75th percentile indicating a significant effect of predicted TAC concentration on event (p=0.0029). From this relationship, the effect of tacrolimus alone can be estimated (Fig 1), and compared to the efficacy of EVR+rTAC to estimate the contribution of EVR. The corresponding HR at M3 was 5.37, 97.5% CI: [2.14, 13.50], p<0.001. Consistent results were observed at both M3 and 12 for all efficacy endpoints (BPAR, tBPAR, and tBPAR/GL/D) and will be presented.
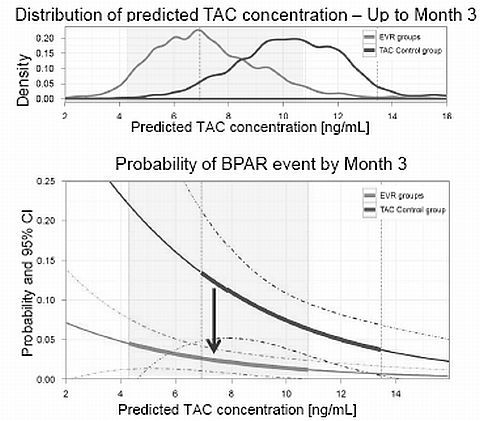
Conclusion: The presented data indicate that EVR at through concentrations of 3-8 ng/mL contributes a relevant effect to significant better efficacy with EVR+Reduced TAC over TAC Control in LTxR.
Junge, G.: Other, NVS, The H2304 Study Group. Dumortier, T.: Other, NVS, The H2304 Study Group. Fischer, L.: Other, NVS, The H2304 Study Group. Kohler, S.: Other, NVS, The H2304 Study Group. Fung, J.: Other, NVS, The H2304 Study Group.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Junge G, Dumortier T, Fischer L, Kohler S, Fung J. Everolimus (RAD001) Treatment Effect in Liver Transplantation – A Rational Approach To Quantify the mTOR Effect [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/everolimus-rad001-treatment-effect-in-liver-transplantation-a-rational-approach-to-quantify-the-mtor-effect/. Accessed January 7, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
