Quantifying Patient Perspectives On Paired Kidney Exchange
1Surgery, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, 2Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B297
Keywords: Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Paired Exchange
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Compatible kidney donor-recipient pairs may not frequently participate in paired kidney exchange (PKE), despite the potential for increased graft survival due to improved HLA matching. Little is understood about patient perspectives on benefits and risks related to PKE participation. We assessed patient perspectives on PKE with the long-term goal of increasing participation of compatible donor-recipient pairs in PKE.
*Methods: Recruited participants included living kidney donor transplant candidates and their donors at a single center (Aug-Nov 2018). We administered a telephone survey to participants prior to receipt of the results of compatibility testing. The survey quantified the risks participants will accept for PKE-related benefits. Survey questions were graduated to determine whether participants would accept greater risk for greater benefit. This included how much additional wait time participants would accept to improve allograft survival of their intended recipient by 1 year and 10 years. Responses were evaluated using a five-level Likert-type scale with the following options: 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years. Responses were averaged for analysis.
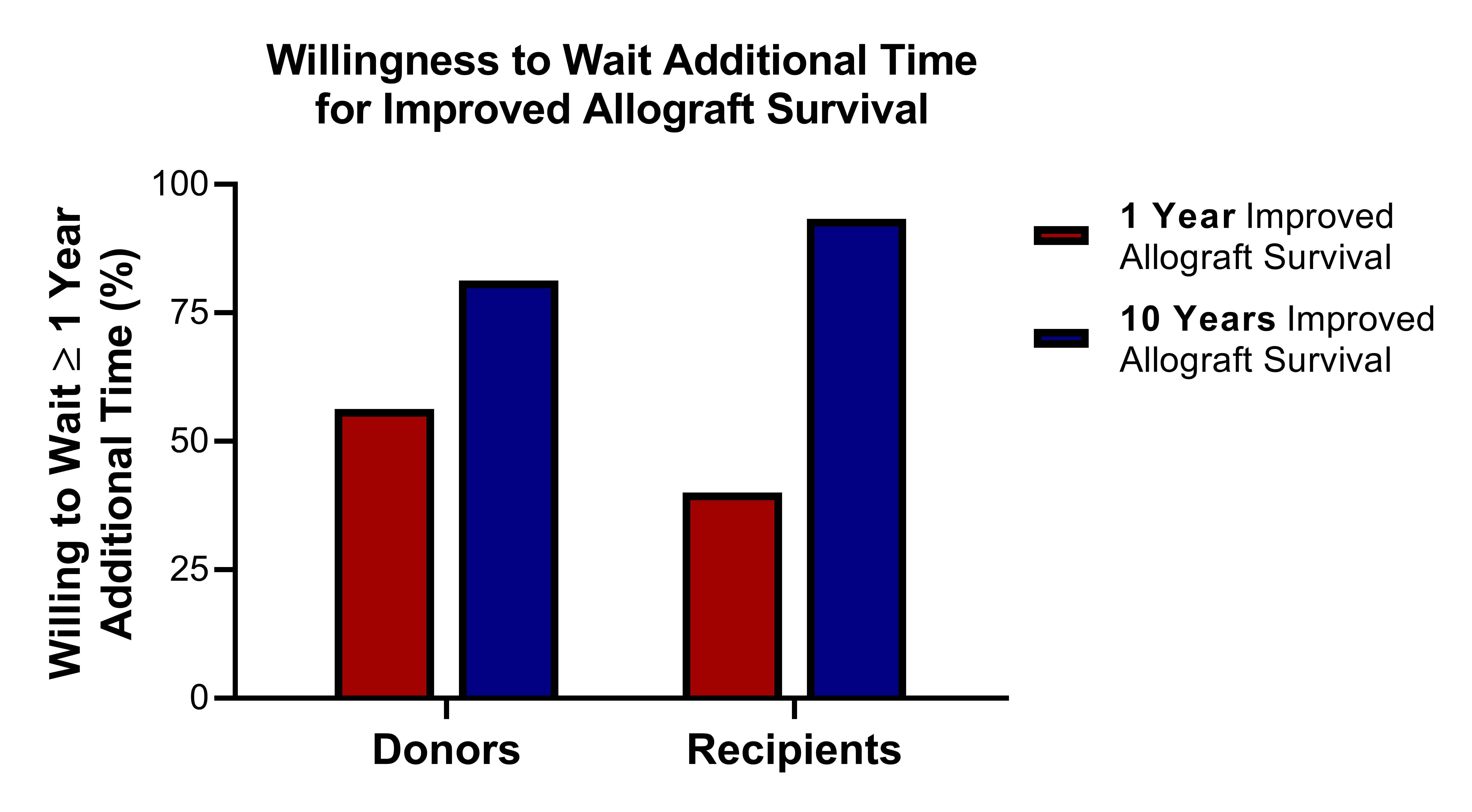
*Results: 16 donor candidates and 15 intended recipients participated in the study. Donors indicated they would wait an average 12.8 additional months to improve allograft survival by 1 year and an average 18.1 additional months to improve allograft survival by 10 years. Recipients indicated they would wait an average 9.1 additional months to improve allograft survival by 1 year and an average 18.6 additional months to improve allograft survival by 10 years. While participants reported they could successfully describe the risks and benefits of PKE, no participant accurately articulated risks to PKE besides surgical complications. 23 of 31 participants reported no familiarity with HLA compatibility or its potential impact on allograft survival.
*Conclusions: Both donors and recipients will accept risk to improve allograft survival, and the effect scales with increasing risk and benefit. However, significant discrepancy exists between patient-reported and actual perspectives on PKE benefits and risks and HLA compatibility. The discrepancy may limit participation among compatible pairs. Transplant centers must educate patients early about PKE to encourage compatible donor-recipient pairs to participate.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Duda M, Houston M, Collins D, Porrett P. Quantifying Patient Perspectives On Paired Kidney Exchange [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/quantifying-patient-perspectives-on-paired-kidney-exchange/. Accessed February 22, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress