Outcomes Associated With Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae (CRKP) in Solid Organ Transplant (SOT) Recipients
1Dept of Pharmacy, Hahnemann University Hospital, Philadelphia
2Dept of Medicine, Drexel University, College of Medicine, Philadelphia
3Dept of Surgery, Drexel University, College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 176
Keywords: Infection
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: ID - Epidemiology, Resistance, Geographic Infections
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 2:15pm-3:45pm
 Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Presentation Time: 3:15pm-3:27pm
Location: Room 115-C
Background: Infection with CRKP is emerging as an important challenge among SOT recipients. Our study aims to describe the epidemiology and clinical outcomes associated with CRKP infections in abdominal SOT recipients.
Methods: A retrospective, observational cohort study was conducted to evaluate adult patients who underwent a successful abdominal SOT (defined as graft survival >30 days) prior to August 2014 with post-SOT CRKP infection. The following outcomes were assessed: clinical cure, 30-day mortality, and infection-related length of stay.
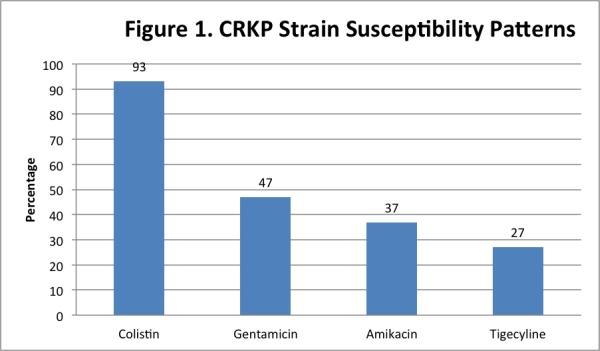
Results: 30 SOT recipients with symptomatic CRKP infections were included in our analysis. Episodes of infection occurred in 17 kidney, 12 liver and 1 dual kidney-liver recipients. Median time to infection post-transplant of 7 months [interquartile range (IQR), 3-50]. Table 1 depicts baseline demographics and primary sites of infection. Secondary bloodstream infections occurred in 4 patients. The overall clinical cure and all-cause 30-day mortality rates were 60% and 17%, respectively. See Figure 1 for susceptibility patterns. Colistin was used as first-line therapy in 45% of patients and the median duration of antibiotic therapy in all patients was 11 days [IQR, 7-15]. Recurrent CRKP infections occurred in 50% of the patient population. Infection related median length of stay was 33 days [IQR, 8-66].
| Age, median, [Interquartile range (IQR)] | 57 (49-66) |
| Male, n (%) | 19 (63) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index, median (IQR) | 5 (4-6) |
| Primary Sites of Infection | |
| Urine, n (%) | 13 (43) |
| Nosocomial pneumonia, n (%) | 11 (37) |
| Bacteremia, n (%) | 3 (10) |
| Intra-abdominal, n (%) | 3 (10) |
Conclusion: CRKP infections pose a serious threat to SOT recipients given its association with increased morbidity, mortality and overall length of stay. Measures to optimize clinical outcomes should include infection control initiatives, rapid diagnostics, and treatment protocols.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bias T, Sharma A, Malat G, Lee D, Doyle A. Outcomes Associated With Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae (CRKP) in Solid Organ Transplant (SOT) Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/outcomes-associated-with-carbapenem-resistant-klebsiella-pneumoniae-crkp-in-solid-organ-transplant-sot-recipients/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
