Preventing Donor Derived Cryptococcal Infections: Should We Screen Potential Organ Donors with a Serum Cryptococcal Antigen? A Cost Analysis
1Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL, 2Washington University, St. Louis, MO, 3Mercy Hospital, Rockford, IL
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A329
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Transplant Infectious Diseases
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Donor-derived cryptococcosis is a rare but deadly infection. Serum cryptococcal antigen testing is a sensitive, specific and inexpensive modality that can be used to screen donors for cryptococcal infection. We performed cost analyses to determine whether donor serum cryptococcal antigen screening is cost effective when balanced against the costs of donor-derived cryptococcosis.
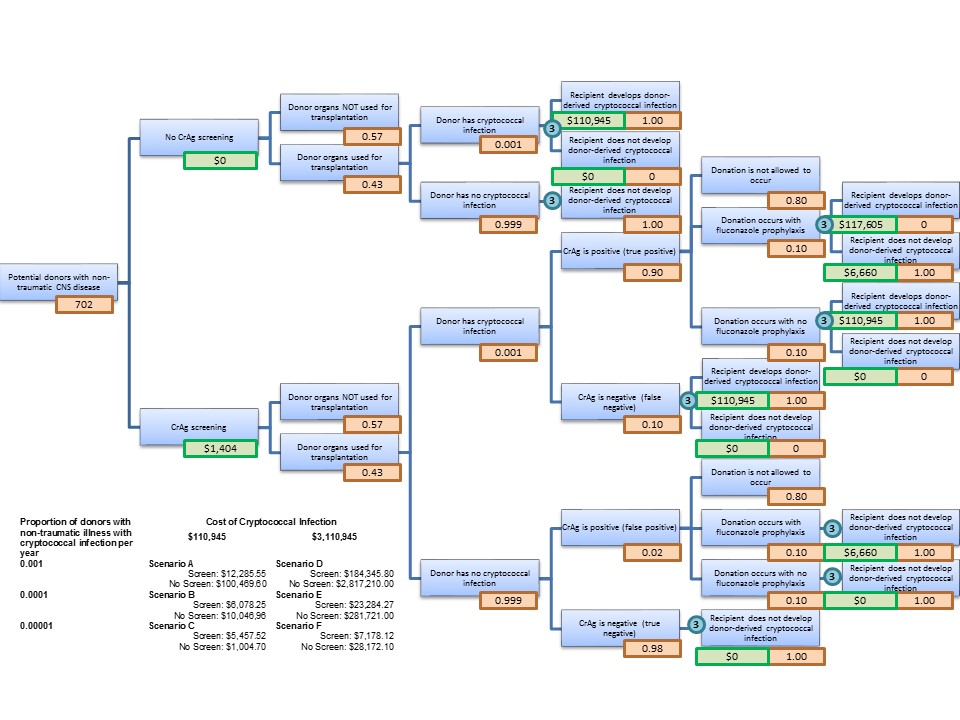
*Methods: We developed a decision tree comparing the average cost of donor serum cryptococcal antigen screening with the average cost of not screening donors, and inputted information on potential organ donors from our local organ procurement organization, serum cryptococcal antigen test characteristics, probabilities of donors having cryptococcosis and recipients contracting donor-derived cryptococcosis with and without fluconazole prophylaxis, cryptococcal infection costs, and fluconazole prophylaxis costs (Figure). The costs of screening versus not screening were first determined for Scenario A where the cost of each serum cryptococcal antigen test was $2, the probability of donor cryptococcal infection was 0.001, and the cost of treating donor-derived cryptococcal infection was $110,945. We then performed sensitivity analyses by varying the probability of donor cryptococcal infection to 0.0001 and 0.00001 (Scenario B and C), and increasing the cost of donor-derived cryptococcal infection by $3,000,000 to include litigation costs and settlements (Scenario D, E and F).
*Results: We found that the average cost of screening 702 potential donors in Scenario A was $12,286, whereas the average cost of not screening donors was $100,470, favoring donor serum cryptococcal antigen screening from a cost perspective. The cost analysis favored cryptococcal antigen screening for all other scenarios, except for Scenario C where the probability of donor cryptococcal infection was 0.00001, and the cost of treating cryptococcal infection was $110,945. The probability of donor cryptococcal infection at which screening would be cost neutral was 0.00006 for cryptococcal infection costs of $110,945, and 0.000002 for costs of $3,110,945.
*Conclusions: Screening potential organ donors with non-traumatic illness for serum cryptococcal antigen may be cost effective when balanced against the costs of donor-derived cryptococcosis. Future studies should address the feasibility of pre-transplant screening programs for donor-derived cryptococcosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Santos C, Ritz E, Rhee Y, George I, Pulvirenti J, Moore N, Hollinger E, Proia L. Preventing Donor Derived Cryptococcal Infections: Should We Screen Potential Organ Donors with a Serum Cryptococcal Antigen? A Cost Analysis [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/preventing-donor-derived-cryptococcal-infections-should-we-screen-potential-organ-donors-with-a-serum-cryptococcal-antigen-a-cost-analysis/. Accessed February 13, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress