Arterial Hypertension and the Use of Antihypertensive Medication in Pediatric Renal Transplant Patients: An Analysis of the CERTAIN Registry
1Department of Pediatric Nephrology, Hannover Medical School, Hanover, Germany
2Division of Pediatric Nephrology, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany
3Department of Medical Sociology, Hannover Medical School, Hanover, Germany.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: D213
Keywords: Hypertension, Kidney transplantation, Pediatric
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session D: Pediatric Clinical Kidney Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Background
Our study aimed to describe the prevalence of hypertension, blood pressure (BP) control and the use of antihypertensive (AH) drugs in pediatric renal transplant patients.
Methods
Casual BP values, number and type of AH medication were analyzed in 284 pediatric patients from the CERTAIN Registry. We selected patients transplanted between 1998 and 2013, for which data entries were available at discharge and at 1 year and/or 2 year follow-up visit. Patients were classified as "normotensive" (if untreated and normotensive), "controlled hypertensive (HT)" (if treated and normotensive), "uncontrolled HT" (if treated and still HT) and "untreated HT" (if untreated and HT). As the age at transplantation ranged from 0.5 to 25 years (median 10.96 years), we calculated SDS values for casual BP, respectively.
Results
At discharge 10% were normotensive, 37% controlled HT, 47% uncontrolled HT and 7% untreated HT. At 1(2) years posttransplant 10(7)% were normotensive, 50(52)% controlled HT, 37(40)% uncontrolled HT and 3(1)% untreated HT (Figure 1a). 48% of the patients were treated with single agent, 29% with a combination of two, and 23% with three to five AH agents. The pattern of drugs use changed over time: At discharge calcium antagonists (31%) and diuretics (25%) were most commonly used, whereas at 1(2) years posttransplant RAAS Blockers with 35(36)% were the most commonly used drugs (Figure 1b).
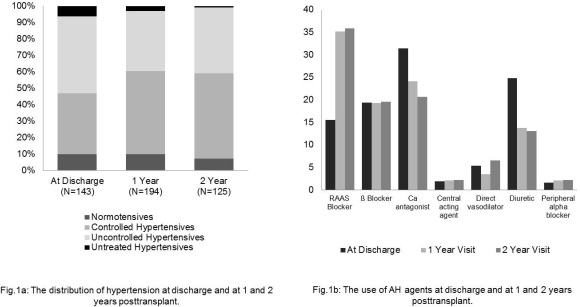
Conclusion
In this cohort most patients were under AH treatment. The use of AH drugs shifted from calcium antagonists and diuretics immediately posttransplant to RAAS blockers and calcium antagonists later on. At discharge 54% of the patients had elevated BP levels, this proportion decreased at 1 year to 40%, and then remained stable. As only a quarter of patients received three or more AH agents, there is potential for further improvement in BP control in this population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sugianto R, Wühl E, Schmidt B, Geyer S, Krupka K, Höcker B, Tönshoff B, Melk A. Arterial Hypertension and the Use of Antihypertensive Medication in Pediatric Renal Transplant Patients: An Analysis of the CERTAIN Registry [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/arterial-hypertension-and-the-use-of-antihypertensive-medication-in-pediatric-renal-transplant-patients-an-analysis-of-the-certain-registry/. Accessed February 17, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
