The Performance of Four Tools for the Prediction of Potential for Organ Donation After Cardiac Death in Neurocritical Patients: A Prospective, Multicenter, Observational Study.
1Organ Transplant Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
2Department of Surgery, Duke University Medical Center, Durham
3Transplant Procurement Management-Donation &
Transplantation institute Foundation, Barcelona, Spain
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C79
Keywords: Donation, Donors, non-heart-beating, Prediction models
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Donor Management: All Organs
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Background Successful donation after circulatory death (DCD) requires identification of patients dieing within limited time after withdrawal of life-sustaining treatment (WLST). We aimed to compare the predictive power of four tools in a prospective, multicenter, observational study.
Methods Data were obtained from consecutive neurocritical patients at four centers in China. The performance of the C-DCD-Nomogram was validated by c-index and calibration plot analysis. C-statistics were calculated to evaluate the predictive ability. The differences in c-statistics between C-DCD-Nomogram and the other models were tested with the method of DeLong et al.
Findings The C-DCD-Nomogram plot performed well in predicting patient death within 30 min, 60 min, 120 min and 240 min after WLST with c statistics of 0[bull]87, 0[bull]88, 0[bull]86, and 0[bull]95, respectively.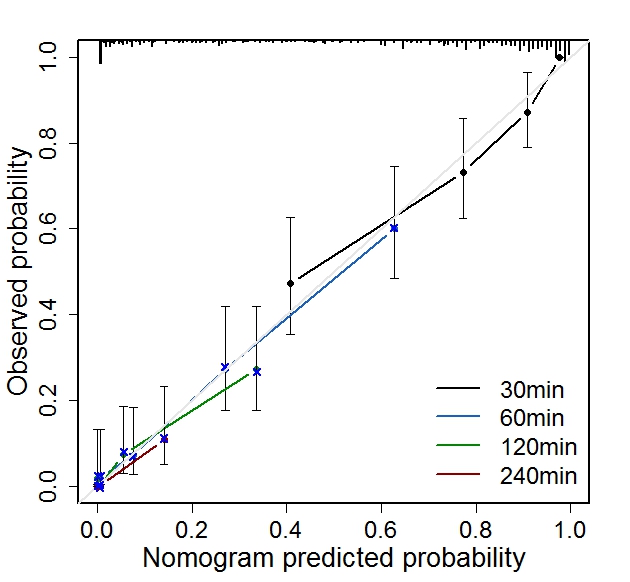 The DCD-N score was a poor predictor of death within 30 min, 60 min, 240 min with c statistics of 0[bull]63, 0[bull]69, and 0[bull]59, respectively, although it performed well in predicting patient death within 120 min with c statistic of 0[bull]73. Neither the UWDCD tool nor the UNOS criteria performed well in predicting patient death within 30 min, 60 min, 120 min and 240 min after WLST (UWDCD tool: 0[bull]48, 0[bull]45, 0[bull]49, and 0[bull]57; UNOS criteria: 0[bull]50, 0[bull]53, 0[bull]51 and 0[bull]63).
The DCD-N score was a poor predictor of death within 30 min, 60 min, 240 min with c statistics of 0[bull]63, 0[bull]69, and 0[bull]59, respectively, although it performed well in predicting patient death within 120 min with c statistic of 0[bull]73. Neither the UWDCD tool nor the UNOS criteria performed well in predicting patient death within 30 min, 60 min, 120 min and 240 min after WLST (UWDCD tool: 0[bull]48, 0[bull]45, 0[bull]49, and 0[bull]57; UNOS criteria: 0[bull]50, 0[bull]53, 0[bull]51 and 0[bull]63).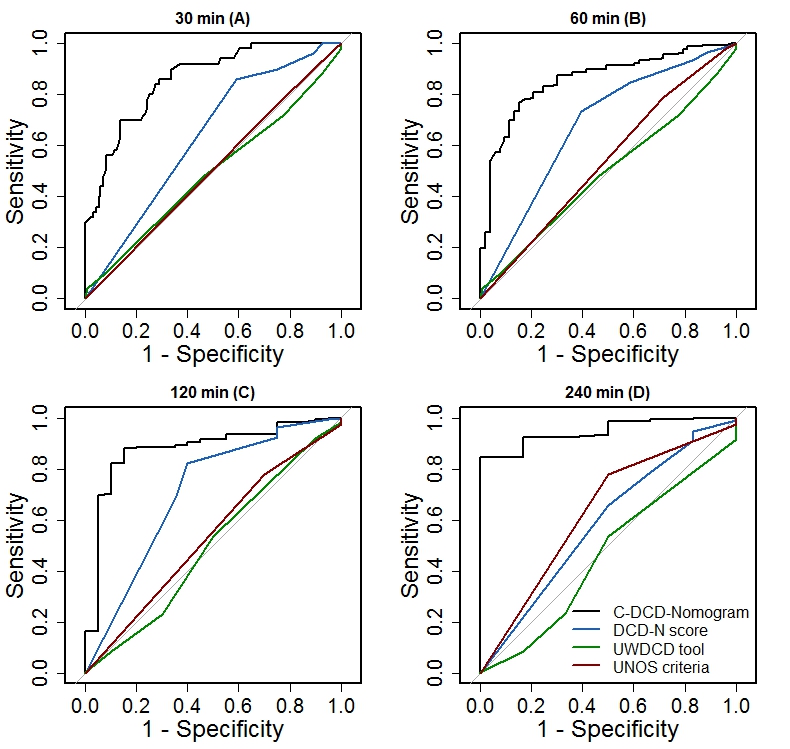 Interpretation The C-DCD-Nomogram is superior to other three models in prediction of patient death within a limited duration after WLST in neurocritical patients, suggesting it a reliable tool to identify potential DCD donors.
Interpretation The C-DCD-Nomogram is superior to other three models in prediction of patient death within a limited duration after WLST in neurocritical patients, suggesting it a reliable tool to identify potential DCD donors.
CITATION INFORMATION: Guo Z, Xu G, Schroder P, Manyalich M, He X, Chen G. The Performance of Four Tools for the Prediction of Potential for Organ Donation After Cardiac Death in Neurocritical Patients: A Prospective, Multicenter, Observational Study. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guo Z, Xu G, Schroder P, Manyalich M, He X, Chen G. The Performance of Four Tools for the Prediction of Potential for Organ Donation After Cardiac Death in Neurocritical Patients: A Prospective, Multicenter, Observational Study. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-performance-of-four-tools-for-the-prediction-of-potential-for-organ-donation-after-cardiac-death-in-neurocritical-patients-a-prospective-multicenter-observational-study/. Accessed February 5, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
