In Vivo Expansion of Donor-Specific Regulatory T Cells by a New Triazolopyrimidine Derivative and Donor-Specific Transfusion
S. Emoto,1 R. Goto,1 S. Shibasaki,1 A. Nagatsu,1 H. Ono,1 R. Igarashi,1 M. Fukai,2 T. Shimamura,3 K. Saiga,4 M. Murakami,5 A. Taketomi,1 S. Todo,6 K. Yamashita.2
1Gastroenterological Surgery 1, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
2Transplant Surgery, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
3Division of Organ Transplantation, Hokkaido University Hospital, Sapporo, Japan
4Nippon Kayaku, Tokyo, Japan
5Institute for Genetic Medecine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan
6Research Institute, St. Mary Hospital, Kurume, Japan.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 136
Keywords: Donor specific transfusion, Graft-infiltrating lymphocytes, Immunosuppression, Mice
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Regulatory T Cells
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 4:00pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:48pm-5:00pm
Presentation Time: 4:48pm-5:00pm
Location: Room 122-AB
Background: We have previously demonstrated that a new triazolopyrimidine derivative, NK026680 (NK) prevents activation/maturation of dendritic cells. This study investigated whether NK together with donor-specific transfusion (DST) induces regulatory T cells (Tregs) and exerts immunomodulatory effect.
Methods: BALB/c (H-2d: donor) mouse-splenocytes (20 million cells) was infused I.V. (DST) to C57BL/6 (B6, H-2b) mice, and NK (40 mg/kg/day) was given P.O. for 14 days. B6 mice received either BALB/c or C3H (H-2k: 3rd-party) mouse cardiac allograft 7 days after DST (day 0) and graft survival time was assessed. CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs were assessed by flow-cytometry.
Results: NK+DST increased Tregs significantly in the spleen after re-stimulation with donor-antigens (Ags:splenocytes), while such Treg increases were neither noted by NK or DST treatment alone nor by re-stimulation with C3H-Ags (Fig.1A). Similarly, NK+DST accelerated accumulation of Tregs into the allograft at day 7 compared with other treatment groups (Fig.1B). Accordingly, NK+DST markedly prolonged allograft survival compared with either DST or NK alone (P<0.01, MST: 75.5, 24.5, or 25.5 days, respectively). In contrast, survival of C3H graft (MST: 22.0 days) did not prolong as long as that of BALB/c graft despite NK+DST treatment (Fig.1C). Finally, administration of depleting anti CD25 mAb (PC61) before NK+DST treatment strongly abrogated the graft survival prolonging effect of NK+DST (MST: 11.0 days) (Fig.1C). 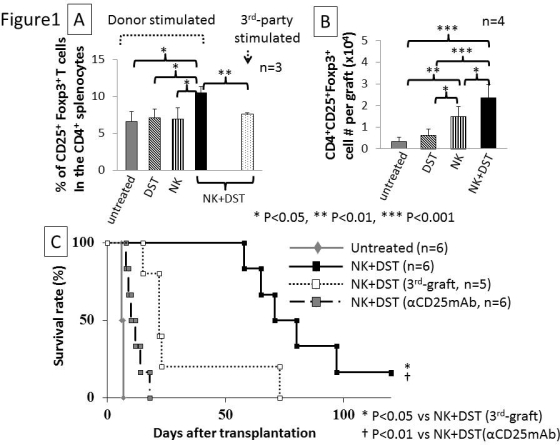
Conclusion: Treatment of NK026680 together with DST, promotes expansion of Ag-specific regulatory T cells and induces a potent immunomodulatory effect in an Ag-specific manner.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Emoto S, Goto R, Shibasaki S, Nagatsu A, Ono H, Igarashi R, Fukai M, Shimamura T, Saiga K, Murakami M, Taketomi A, Todo S, Yamashita K. In Vivo Expansion of Donor-Specific Regulatory T Cells by a New Triazolopyrimidine Derivative and Donor-Specific Transfusion [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/in-vivo-expansion-of-donor-specific-regulatory-t-cells-by-a-new-triazolopyrimidine-derivative-and-donor-specific-transfusion/. Accessed February 15, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
