Performance-Based vs. Self-Reported Functional Assessment on Outcomes After Kidney Transplant.
Renal and Pancreas Transplant Department, Saint Barnabas Medical Center, Livingston, NJ
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 345
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Morbidity, Mortality
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Clinical Complications 2
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, May 1, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: E354b
Reduced functional capacity (FC) is associated with poor outcomes and early hospital readmission after kidney transplant (KT). The aim of the study was to determine if objective and subjective measures of FC are congruent and associated with outcomes after KT.
Medical records of patients who received a KT at a single center were reviewed. At the time of transplant FC was obtained by: 1)Short Form 4a PROMIS survey on physical function and 2)hand-grip (HG) strength measurement using the Jamar dynamometer. The average of 2 grip tests was used for analysis. Patients were defined as frail if either of the following occurred: 1) > -1 standard deviation (SD) below normative range on HG testing, 2)scored < 12 on the survey.
There were 58 patients with a mean age of 50.8 years. 21 patients (36.2%) were within normative range for HG strength and 37 (63.8%) fell > -1 SD below normative range. 39 patients (67.2%) scored > 13 on the survey while 19 (32.8%) scored < 12. Among patients with frail HG strength, 23 had a survey score of > 13 (62.2%). Among patients with a survey score of > 13, 23 (59.0%) had a frail HG test. Re-hospitalization rate within the first 90 days was 32.4% in the frail HG group vs. 19.0% in the non-frail HG group. Re-hospitalization rate within the first 90 days was 18.9% in the frail survey group vs. 42.9% in the non-frail survey group.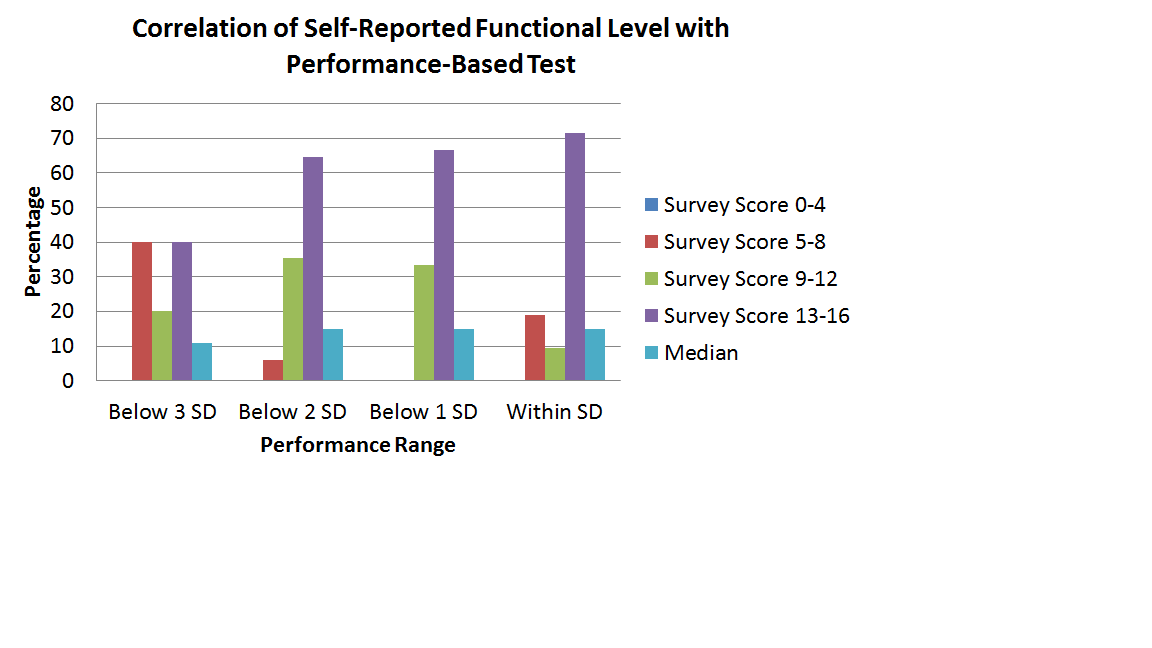
 Self-reported assessments of frailty do not appear to correlate with an objective measure in KT recipients. KT recipients tend to overestimate their FC. An objective measurement of frailty may be more accurate in predicting early readmission rate after KT. A larger cohort of patients should be followed to confirm these preliminary findings and to determine if patient mortality is correlated with objective and/or subjective measures of frailty.
Self-reported assessments of frailty do not appear to correlate with an objective measure in KT recipients. KT recipients tend to overestimate their FC. An objective measurement of frailty may be more accurate in predicting early readmission rate after KT. A larger cohort of patients should be followed to confirm these preliminary findings and to determine if patient mortality is correlated with objective and/or subjective measures of frailty.
CITATION INFORMATION: Tibaldi K, Dhillon N, Goldberg R, Paniagua H, Patel A. Performance-Based vs. Self-Reported Functional Assessment on Outcomes After Kidney Transplant. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tibaldi K, Dhillon N, Goldberg R, Paniagua H, Patel A. Performance-Based vs. Self-Reported Functional Assessment on Outcomes After Kidney Transplant. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/performance-based-vs-self-reported-functional-assessment-on-outcomes-after-kidney-transplant/. Accessed February 19, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
