Pre-Existing Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Insufficiently Controlled Post-Transplant HbA1c in Kidney Transplantation.
F. Halleck, D. Khadzhynov, L. Lehner, E. Schrezenmeier, M. Duerr, A. Kleinsteuber, K. Budde, O. Staeck.
Nephrology, Charité
University, Berlin, Germany.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B237
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Metabolic complications, Outcome, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background Limited data have been reported on the outcomes of kidney transplant recipients (KTR) with pre-existing diabetes mellitus type 2 (preDM) at time of transplantation and the influence of HbA1c levels post-transplant.
Methods This retrospective study included 1164 KTR transplanted 1996-2014. preDM and HbA1c levels 6-24 months post-transplant were determined. Cox proportional hazards models were fitted to examine the association of preDM, HbA1c and time-to-event outcomes with inclusion of recipient age, sex, time on dialysis, prior kidney transplantation, donor age, HLA-mismatches and cold ischemia time.
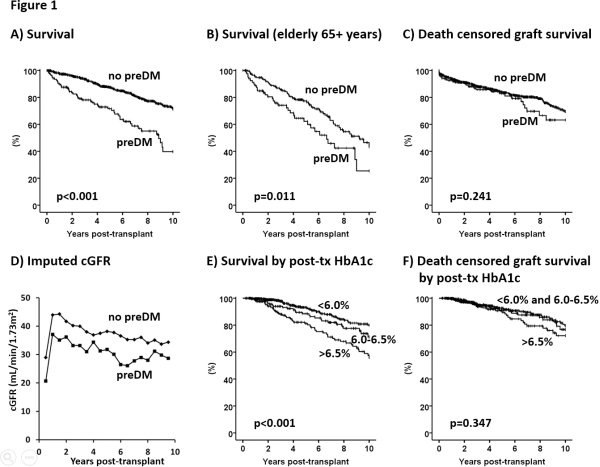
Results Mean age was 51yrs, mean post-transplant follow-up 6.0yrs. 16% of the KTR had preDM, 9% preDM with diabetic end-organ damage (retinopathy, neuropathy or nephropathy). KTR with preDM were older (63 vs 51yrs, p<0.001), had a larger BMI (28 vs 25 kg/m2), shorter time on dialysis (4.3 vs 5.8yrs, p<0.001), lower rate of previous transplantation (9 vs 18%, p=0.009) and more HLA mismatches (3.2 vs 2.5, p<0.001) compared to KTR without preDM. Overall KTR with preDM showed poorer patient survival (Fig 1A). Subanalysis of 262 elderly KTR with preDM showed a median survival time of 9.1yrs in the group with preDM vs 6.4yrs in the group without preDM (Fig 1B). There was no significant correlation between preDM and graft failures (Fig 1C). KTR with preDM had a significantly lower cGFR over time (Fig 1D). Multivariate analysis revealed that preDM was a main driver of mortality (HR 1.78; p=0.001). The relative hazard of death was considerably higher in KTR with preDM and diabetic end-organ damage (HR 2.87; p=0.001). KTR with an HbA1c level >6.5% within 6-24months post-transplant showed a significantly higher mortality while graft survival was not affected (Fig 1E-F). Multivariate analysis confirmed that HbA1c levels >6.5% 6-24 months post-transplant are an independent predictor of death (HR 1.7; p=0.05).
Conclusion preDM is a independent risk factor for death in KTR in all age categories. These data support the importance of post-transplant HbA1c control to lower mortality.
CITATION INFORMATION: Halleck F, Khadzhynov D, Lehner L, Schrezenmeier E, Duerr M, Kleinsteuber A, Budde K, Staeck O. Pre-Existing Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Insufficiently Controlled Post-Transplant HbA1c in Kidney Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Halleck F, Khadzhynov D, Lehner L, Schrezenmeier E, Duerr M, Kleinsteuber A, Budde K, Staeck O. Pre-Existing Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Insufficiently Controlled Post-Transplant HbA1c in Kidney Transplantation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/pre-existing-diabetes-mellitus-type-2-and-insufficiently-controlled-post-transplant-hba1c-in-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
