Socioeconomic Status and Readmission Following Kidney Transplant.
Transplant Surgery, Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B71
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Disparities in Access and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Our group has previously demonstrated that 31% of kidney transplant recipients are readmitted within 30 days of discharge from the original hospitalization. Patient-level contributors such as demographics and comorbidities, as well as center-level contributors, have been studied but inadequately predict which patients are at risk of readmission. The goal of this study was to investigate if measures of socioeconomic status provided further insights into readmission risk.
METHODS: USRDS data for all Medicare primary adult kidney transplant recipients between 1999-2011 were studied for readmission within 30 days. Patients were excluded if they died during their original transplant admission or within 30 days without readmission. Our exposure of interest was socioeconomic status as defined by the American Health Quality Association measured by quartile, components including proportional crowding, poverty, property value, median income, college education, high school education, and unemployment. Modified Poisson regression was used to determine the association between socioeconomic status and readmission, adjusting for previously described risk factors. 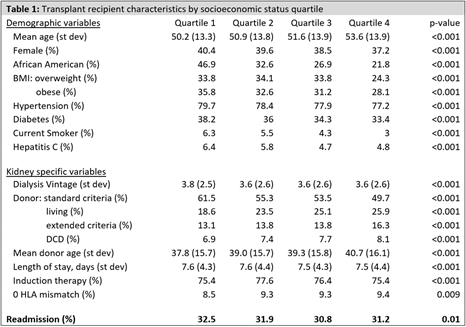
RESULTS: We found no independent associations between socioeconomic status and readmission. Each component of the socioeconomic index was also explored in a separate adjusted model, and only proportional crowding had a statistically significant association with readmission (IRR 0.69 CI 0.49-0.98, p=0.04). 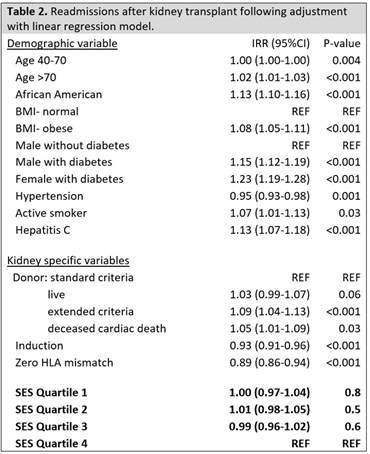
CONCLUSION: There were no differences found in rate of readmission between socioeconomic status quartiles, suggesting that overall, socioeconomic status has no independent effect on readmission rate following kidney transplantation.
CITATION INFORMATION: DiBrito S, King E, O'Hare M, Segev D. Socioeconomic Status and Readmission Following Kidney Transplant. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
DiBrito S, King E, O'Hare M, Segev D. Socioeconomic Status and Readmission Following Kidney Transplant. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/socioeconomic-status-and-readmission-following-kidney-transplant/. Accessed March 6, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
